Gum Grafting
Gum Grafting
What is Gum Grafting?
What is Gum Grafting?
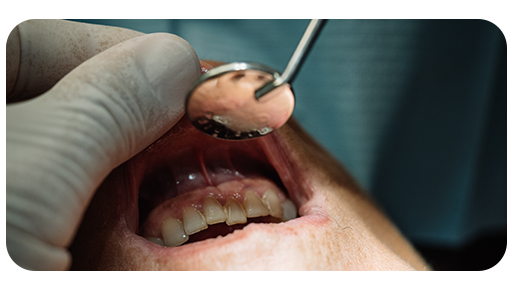
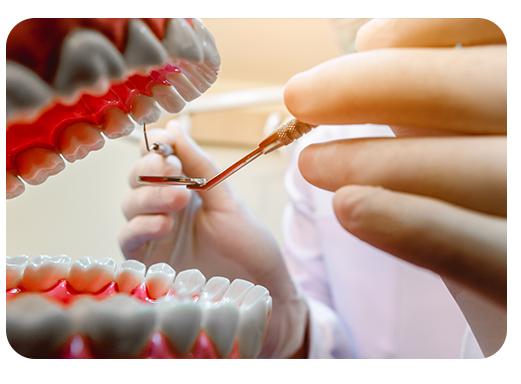
Why is Gum Grafting Performed?
Why is Gum Grafting Performed?
How is Gum Grafting Performed?
How is Gum Grafting Performed?
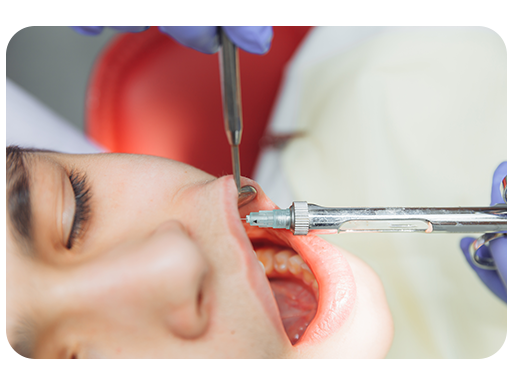
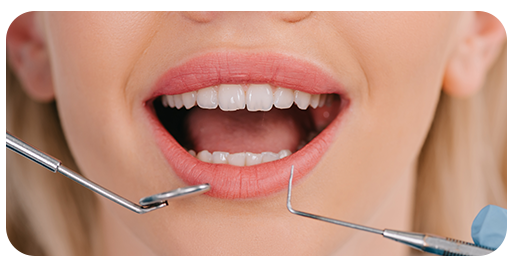
Who is a Candidate for Gum Grafting?
Who is a Candidate for Gum Grafting?
Post-Procedure Care for Gum Grafting
Post-Procedure Care for Gum Grafting
Is Gum Grafting a Safe Procedure?
Is Gum Grafting a Safe Procedure?
How Long Does Gum Grafting Take?
How Long Does Gum Grafting Take?


Will There Be Pain After Gum Grafting?
Will There Be Pain After Gum Grafting?
Is Gum Grafting Permanent?
Is Gum Grafting Permanent?

Conclusion Gum Grafting
Conclusion Gum Grafting
Frequently Asked Questions
Smoking adversely affects oral health by: • Increasing the risk of gum disease • Delaying healing after dental procedures • Causing bad breath and staining teeth • Elevating oral cancer risk Quitting smoking improves oral health and the success of dental treatments.
Bruxism involves involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth, often during sleep. Possible causes: • Stress and anxiety • Misaligned teeth • Sleep disorders Treatment: • Night guards to protect teeth • Stress management strategies • Orthodontic treatments if misalignment is a factor
Gum recession occurs when the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing roots and causing sensitivity. Treatment Options: • Deep cleaning (scaling and root planning) • Gum graft surgery in severe cases • Use of desensitizing toothpaste to manage symptoms Early treatment helps preserve gum health and prevent tooth loss.
Pregnancy can affect oral health due to hormonal changes, increasing the risk of: • Gum inflammation (pregnancy gingivitis) • Pregnancy tumors (harmless overgrowths on gums) • Enamel erosion from morning sickness Maintaining regular brushing, flossing, and safe dental check-ups during pregnancy is crucial for both mother and baby’s health.
Diastema (Gap Between Teeth) and Its Treatment
